Lecture §
Conflict, Stress & Power §
- Peterson’s General Model of Conflict:
Beginging ==[Engagement]==> Middel ==> Termiantion
- Beginnings:
- Predisposing factors – increase likelihood of conflict
- Conflict of interest, situational stress, emotion and mood, personality, attachment style, stage in life
- Instigating events: Interference with goal-directed action
- Criticism, illegitimate demands, rebuffs, cumulative annoyances
- Engagement vs. Avoidance
- Engagement: Issue perceived as significant but solvable
- Avoidance: Issue perceived as trivial or insolvable,
conflict end
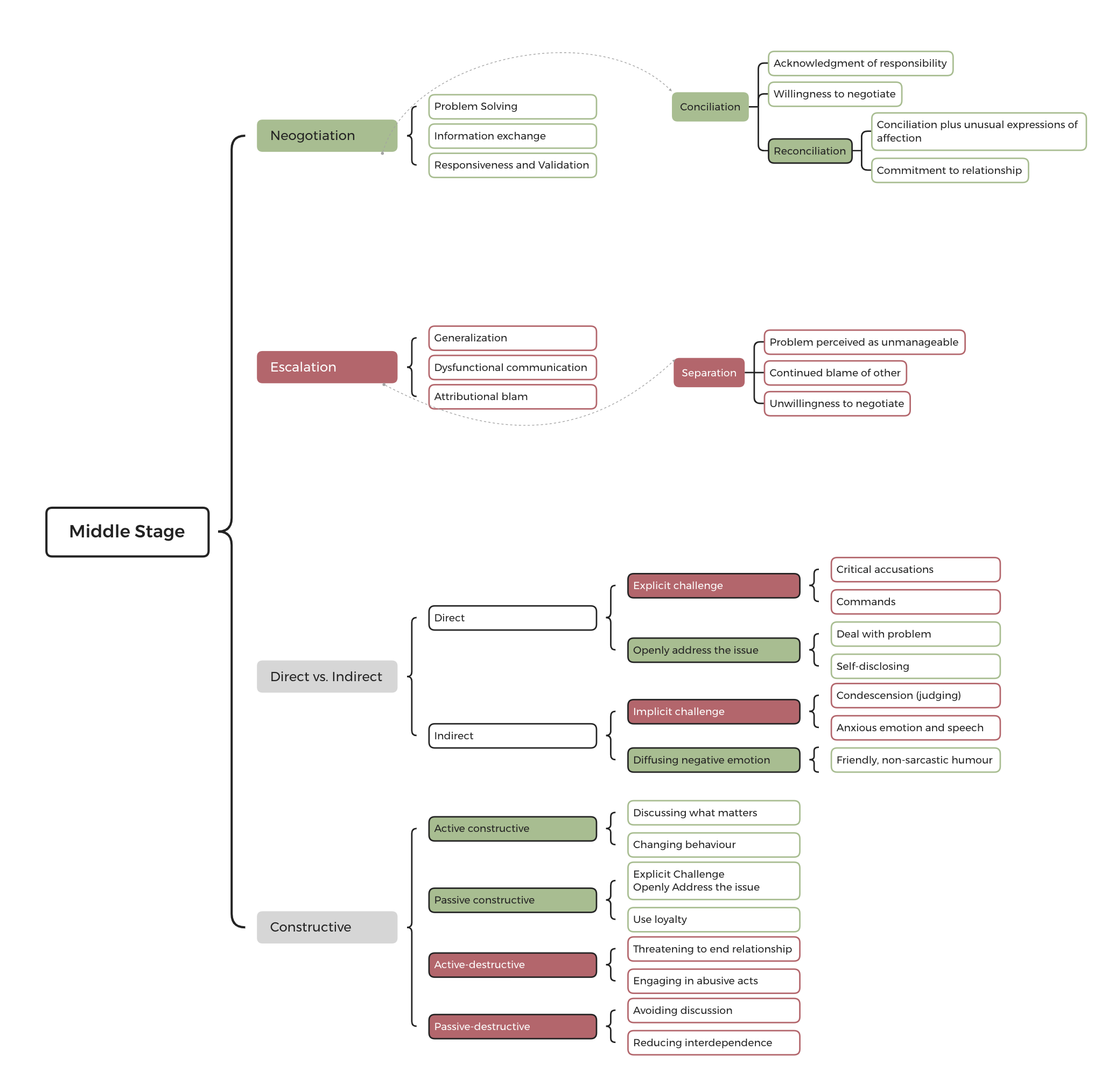
- Middle
- Termination
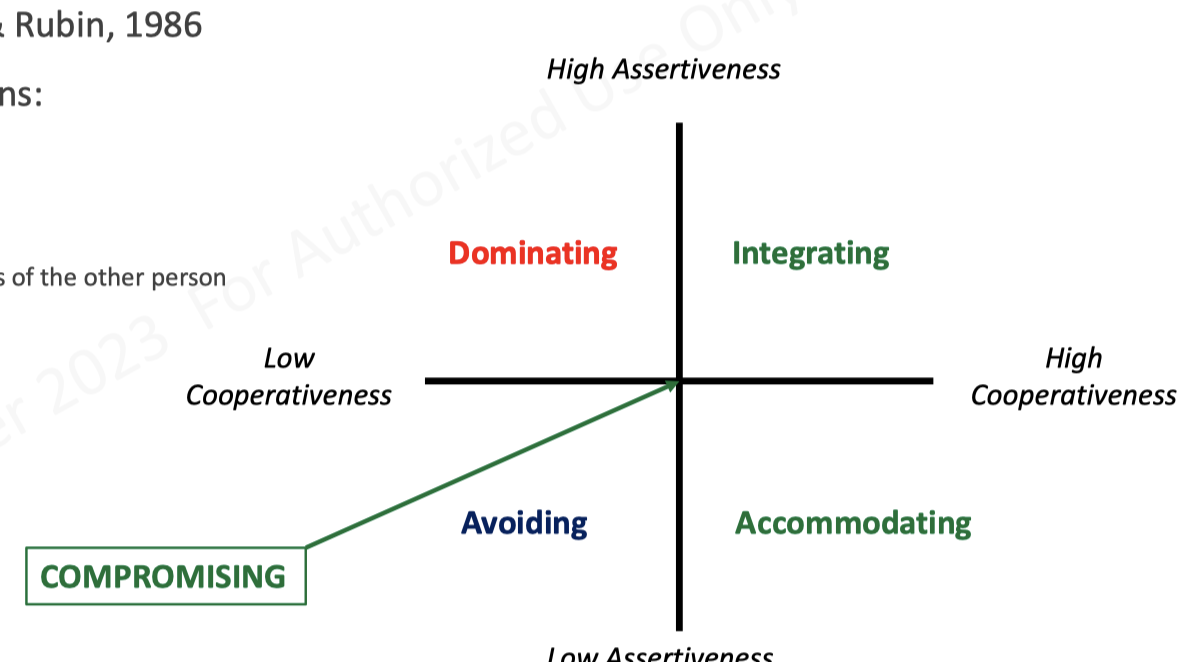
- Dual-concern theory
Relationship Stress §
- Rejection
- Relational devaluation: depends on levels of acceptance and/or rejection
- Early rejection experiences have long term effects
- Reason for rejection: need to belong, feelings of self-worth, perceptions of control
- Responses
Behavioural response
- Self-defeating behaviours (Procrastination), less self-control, more aggression
- Prosocial behavioural (自卑?讨好式社交?)
Cognitive response
- Deconstructed states (lack of meaning and control), less intelligent thought, more attention to social information
Emotional response
- Confusion, hurt feelings, sadness, anger, anxiety
- Ostracizes: justification for behaviour, damaging the relationship
- Criticism: reduce felt security
- Jealousy
- Definition: Potential loss of a valued relationship to a real or imagined rival
- 2 Types
- Reactive jealousy: awareness of an actual threat to a valued relationship
- Suspicious jealousy: one’s partner has not been misbehaving and one’s suspicions do not fit the facts
- Betrayal
- Definition: any act that violates the norms of benevolence, loyalty, respect and trustworthiness within a relationship
Active Studying §
Summarize today’s lecture §
- [::Most important/focused topic]
- [::Most difficult part, why, how to resolve]
What part I didn’t understand, next step actions? §