Reading §
Questions §
Quizlet
Chapter 1 §
- Business
- What activity lies at the heart of every business endeavour?
- Trade (exchange between buyer and seller)
- Profit-seeking activities that brings goods and services to the economic market.
- What are the primary objectives of a not-for-profit organization?
Public service > profit, need to raise money for operation
- Factors of production
- Identify the four basic inputs to an economic system
- Natural Resource
- Capital
- Human Resource
- Entrepreneurship
- List 4 types of capital
- Information
- Tool
- Technology
- Physical facilities
- Private enterprise system
- What is an alternative term for the private enterprise system?
- What is the most basic freedom under the private enterprise system?
- Right to private property
- What is an entrepreneur?
- A person that is willing to take the risks to start, own, and operate a business
- History of business
- What is the 7 ears in business
- Colonial Period
- Industrial Revolution
- Industrial Entrepreneurship
- Product era
- Marketing era
- Relationship era
- Social era
- What was the Industrial Revolution?
Independent Skilled Worker -> Factory Mass-Production System- Started around 1750 in England
- During which era was the idea of branding developed?
- What is the difference between transaction management and relationship management?
- Transaction management: (product focus) building, promoting, and selling produce to cover costs
- Relationship management: (customer focus) maintain ongoing ties with customer
- Workforce trend
- What are the 3 significant changing trend in workforce
- Aging and shrinking labour
- Diverse workforce
- Work focus shift toward service/information
- Define outsourcing, offshoring, and nearshoring
- Outsourcing: actively allow production/service by venders (供应商)
- Offshoring: move business operation overseas to lower cost
- Nearshoring: offshoring near home base
- Describe the importance of collaboration and employee partnership.
- Collaboration: increase efficiency and possibly more creative ideas
- Employee partnership: teamwork, creative thinking, problem solving as innovation as a group instead of doing on an individual biases (due to quickly changing job market)
- Skills of contemporary manager
- Why is vision an important managerial quality?
- Helps firms to adapt and innovate
- What is the difference between creativity and critical thinking?
- Creativity: new solutions to problems
- Critical thinking: problem solving & analysis ability
- Admiration of firms
- Define business ethics and social responsibility.
- Business ethics: standard conduct & moral codes for for business operation & work environment
- Social responsibility: contribution (resources) to society & natural environment
- Identify three criteria used to judge whether a company might be considered admirable.
- Profitability: solid profit, stable growth
- Safety: safe & challenging work environment, good business ethics and social responsibility
- Quality: High-quality goods/service
Chapter 3 §
- Discuss microeconomics and the forces of demand and supply
- What is the differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics
- Microeconomics: the study of economics among individual consumers, families, and business
- Microeconomics: the study of economics among governments and countries
- What is supply and demand, what are some factors affecting them?
- Demand: willingness/ability of buyers to purchase good/service
- Depends on customer (preferences, numbers, their income, expectations), market (price for substitute/complementary good)
-
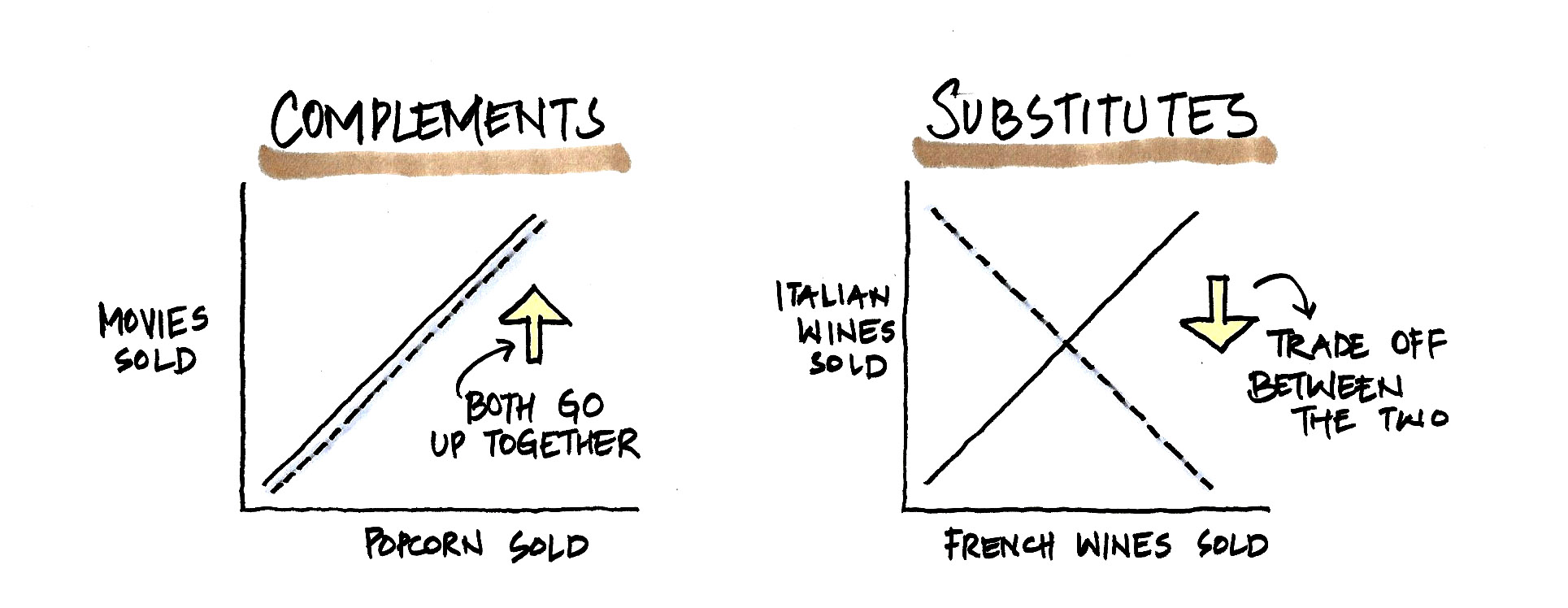
- Supply: willingness/ability of businesses to offer good/services
- Depends on the cost of (inputs, technology resources, taxes), and the number of suppliers in the market
- Explain demand and supply curves.
- Demand curve: a graph that shows the amount of product that buyers will purchase on different prices
- Supply curve: a graph that shows the amount of product the sellers will offer on different prices (regardless of demand)
- How do factors of production affect the overall supply of goods and services?
- A change in the cost or availability of any of the factors of production can shift the entire supply curve by either increasing or decreasing the amount available at every price.
- Describe macroeconomics and the 3 major types of economics systems
- What are the 3 major types of economics systems
- Private enterprise system
- Individual business pursue their own interests without much governmental restriction
- Capitalism
- Planned economics
- Government has control over business ownership, profits, and resources needed to accomplish governmental/social goals
- Communism: a planned economics system without private property
- Mixed economies
- Blends government ownership and private enterprise
- What are the 4 basic types of competition in a private enterprise system?
- Pure competition
- A market structure, large number of buyers and sellers exchange similar products, no single participant has a large influence on price
- Monopolistic competition
- A market structure, large number of buyers and sellers exchange differentiated (dissimilar) products, each participant has some control over price
- Oligopoly competition
- Market situation, few sellers compete (high startup costs keep out new competitors)
- Monopoly competition
- One seller controls trade in a good/service, no substitute for buyer
- What economic system is the Canadian economy based on?
- What is privatization?
- Conversion of government-owned-operated agencies to private
- Economic performance
- Explain how productivity, price level changes, and employment levels affect economic performance
- Productivity rise
--> increase economy’s growth + increase citizen wealth
- Price level changes (inflation/deflation): indicator of economy’s stability
- Canadian gov. measures this by using the
Consumer Price Index
- Unemployment rate: the percentage of total labour force (want, but unable to find jobs)
- Describe the 4 stages of business cycle
- Prosperity
- Strong consumer confidence
- Recession
- Depression
- Economic slowdown over a long period of time
- Recovery
- Consumer start spending again
- High business activity
--> lower unemployment
- What do economists use to measure economy performance
- Gross domestic produce
- The general level of prices, the core inflations rate, the Consumer Price Index, and unemployment rate among other things
- Manage economy’s performance
- Discuss how monetary polity and fiscal policy are used to manage economy?
- Monetary policy
- Government’s plan to control the size of the nation’s money supply
- Expansionary vs. Restrictive
- Increase money supply
--> decrease interest --> increase investment demand
- Reduce money supply
--> increase interest --> decrease investment demand (control overexpansiona)
- Can be used to encourage growth or control inflation
- Fiscal policy
- Government revenues and expenditures(支出) decisions
- Decrease spending
+ increase taxes --> economic expansion (inflation)
- Gov. need to raise spending money through taxes
- What are the 3 primary sources of gov. fund?
- Taxes
- [?] 2. Fees (intergovernment/utility revenue)?
- Borrowing (interest)
- Why is no country an economic island today?
- No business or country is an economic island because many goods and services travel across national borders. Many companies are now becoming multinational firms.
- Describe 2 ways in which global expansion can benefit a Canadian firm.
- A firm can benefit from global expansion by attracting more customers and by using less expensive labour and production to produce goods and services.
Lecture §
PDF:
- Sean mullin
- Say your full name when meet people
- Goal for personal brand: stand out
- Amplify authenticity, people buy YOU first
- Networking is who knows you (what you are doing to get known)
- Does it feel good to talk to you
- Put the focus on the other person during conversation
Questions §
