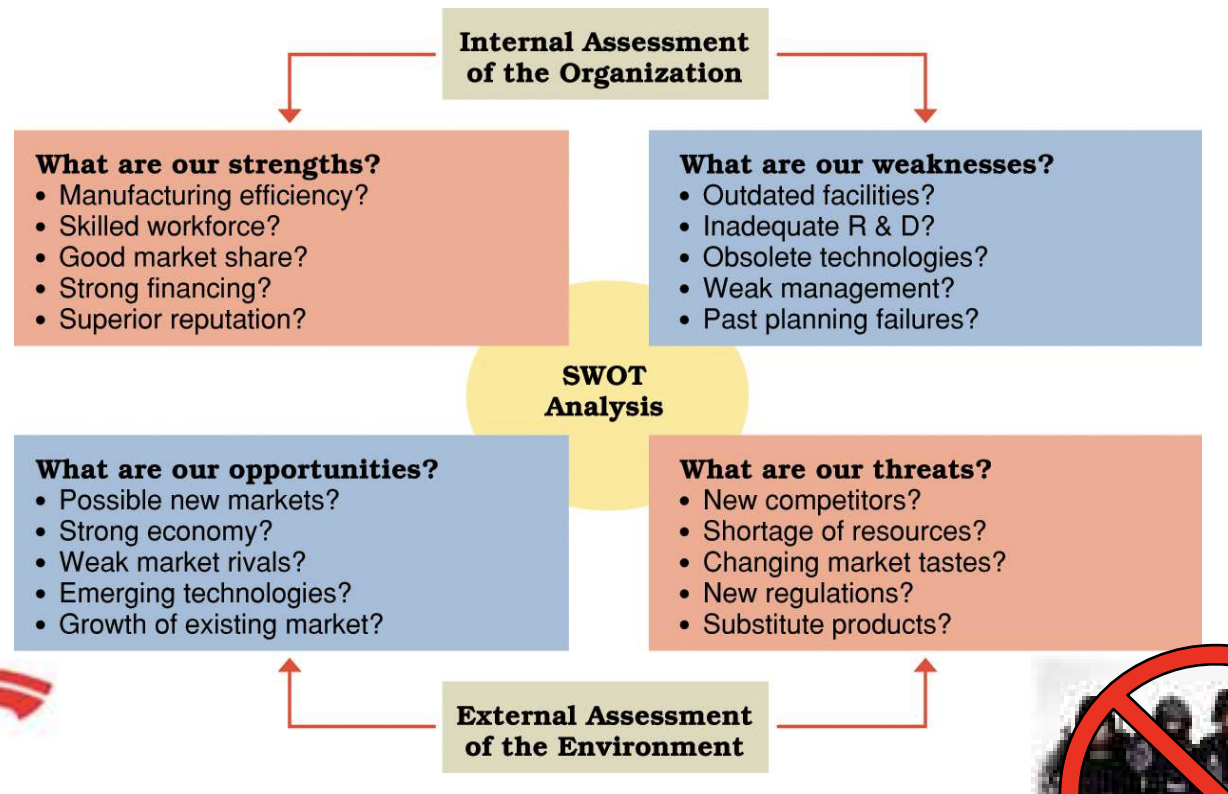
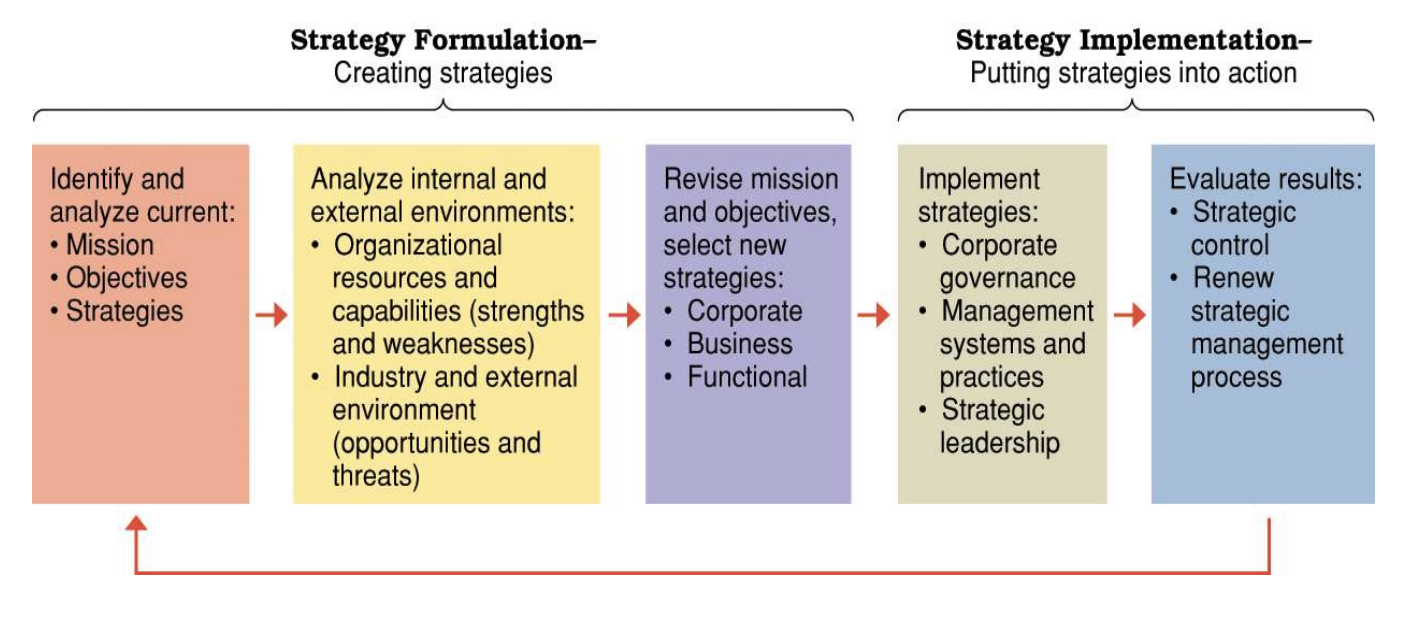
Reading §
Chapter 15 §
- Accounting
- Define accounting.
- Accounting is the process of measuring, interpreting, and communicating financial information that describes the status and operation of an organization and aids in decision making.
- Who uses accounting information?
- Managers in all types of organizations use accounting information to help them plan, assess performance, and control daily and long-term operations.
- Outside users of accounting information include government officials, investors, creditors, and donors.
- What three business activities involve accounting?
- Financing
- Investing
- Operating activities.
- Accounting professionals
- List the three services offered by public accounting firms.
- Auditing 审计
- Management consulting
- Tax services.
- What tasks do management accountants perform?
- Management accountants work for an organization. They are responsible for collecting and recording financial transactions and for preparing and interpreting financial statements.
- Accounting system
- Define GAAP.
- GAAP stands for generally accepted accounting principles. It is a set of standards, or guidelines, that accountants follow when recording and reporting financial transactions.
- What is the role played by the AcSB?
- The Accounting Standards Board (AcSB) is an independent body made up of accounting professionals. It is primarily responsible for evaluating, setting, and modifying Canadian GAAP related primarily to private and not-for-profit organizations. Note that publicly accountable organizations are required to follow IFRS
- Accounting cycle
- List the steps in the accounting cycle.
- Recording transactions
- Classifying the transactions
- Summarizing the transactions
- Using the summaries to produce financial statements.
- What is the accounting equation?
- The accounting equation states that assets (what a firm owns) must always equal liabilities (what a firm owes) plus owners’ equity (the owners’ investments in the firm). An increase or decrease in an asset must be balanced by an increase or decrease in liabilities, owners’ equity, or both.
- Briefly explain double-entry bookkeeping.
- Double-entry bookkeeping requires every transaction to be balanced by another transaction.
- 4 principle financial statements
- List the four financial statements.
- The balance sheet
- The income statement
- The statement of changes in equity
- The statement of cash flows.
- How is the balance sheet organized?
- Assets (what a firm owns) are shown on one side of the balance sheet and are usually listed in a downward order based on their convertibility into cash. On the other side of the balance sheet are claims to assets, liabilities (what a firm owes), and owners’ equity (the owners’ investments in the firm). Claims are usually listed in the order in which they are due. For example, liabilities are listed before owners’ equity. Assets always equal liabilities plus owners’ equity.
- Define accrual accounting.
- Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they occur, not when cash actually changes hands. Most companies use accrual accounting to prepare their financial statements.
- Financial ratios
- List the four categories of financial ratios.
- Liquidity
- Activity
- Profitability
- Leverage
- Assets=Liabilities+Owner’s Euity
- Define the following ratios: current ratio, inventory turnover, net profit margin, and debt ratio.
- | Category | Ratio | Description |
| -------------------- | ------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| Liquidity ratios | Current ratio | Current assets÷Current Liabilities |
| | Quick (acid-test) ratio | [Current assets−Inventory−Prepaid expenses]÷Current liabilities |
| Activity ratios | Inventory turnover | Cost of goods sold÷Average inventory |
| | Receivables turnover | Credit sales÷Average accounts receivable |
| | Total asset turnover | Revenue OR Sales÷Average total asset |
| Leverage ratios | Debt ratio | Total liabilities divided by total assets |
| | Long-term debt to equity | Long-term debt divided by owners’ equity |
| Profitability ratios | Gross profit margin | Gross profit divided by revenue or sales |
| | Net profit margin | Net profit divided by revenue or sales |
| | Return on equity | Net profit divided by average owners’ equity |
- Current ratio equals current assets divided by current liabilities
- Inventory turnover equals cost of goods sold divided by average inventory
- Net profit margin equals net income divided by sales
- Debt ratio equals total liabilities divided by total assets.
- Budgets
- What is a budget?
- A budget is a planning and control tool that reflects the firm’s expected sales revenues, operating expenses, cash receipts, and cash expenses.
- How is a cash budget organized?
- Cash budgets are usually prepared monthly. Cash receipts are listed first. They include cash sales and the collection of past credit sales. Cash outlays, or cash expenses, are listed next. These include cash purchases, payment of past credit purchases, and operating expenses. The difference between cash receipts and cash outlays is net cash flow.
- Online accounting
- How are financial statements adjusted for exchange rates?
- An exchange rate is the value of one country’s currency in terms of the currencies of other countries. Fluctuations, the ups and downs, of exchange rates create either gains or losses for global companies. Data about international financial transactions must be translated into the currency of the country where the parent company resides.
Chapter 17 §
- Financial managers
- What is the structure of the finance function at the typical firm?
-
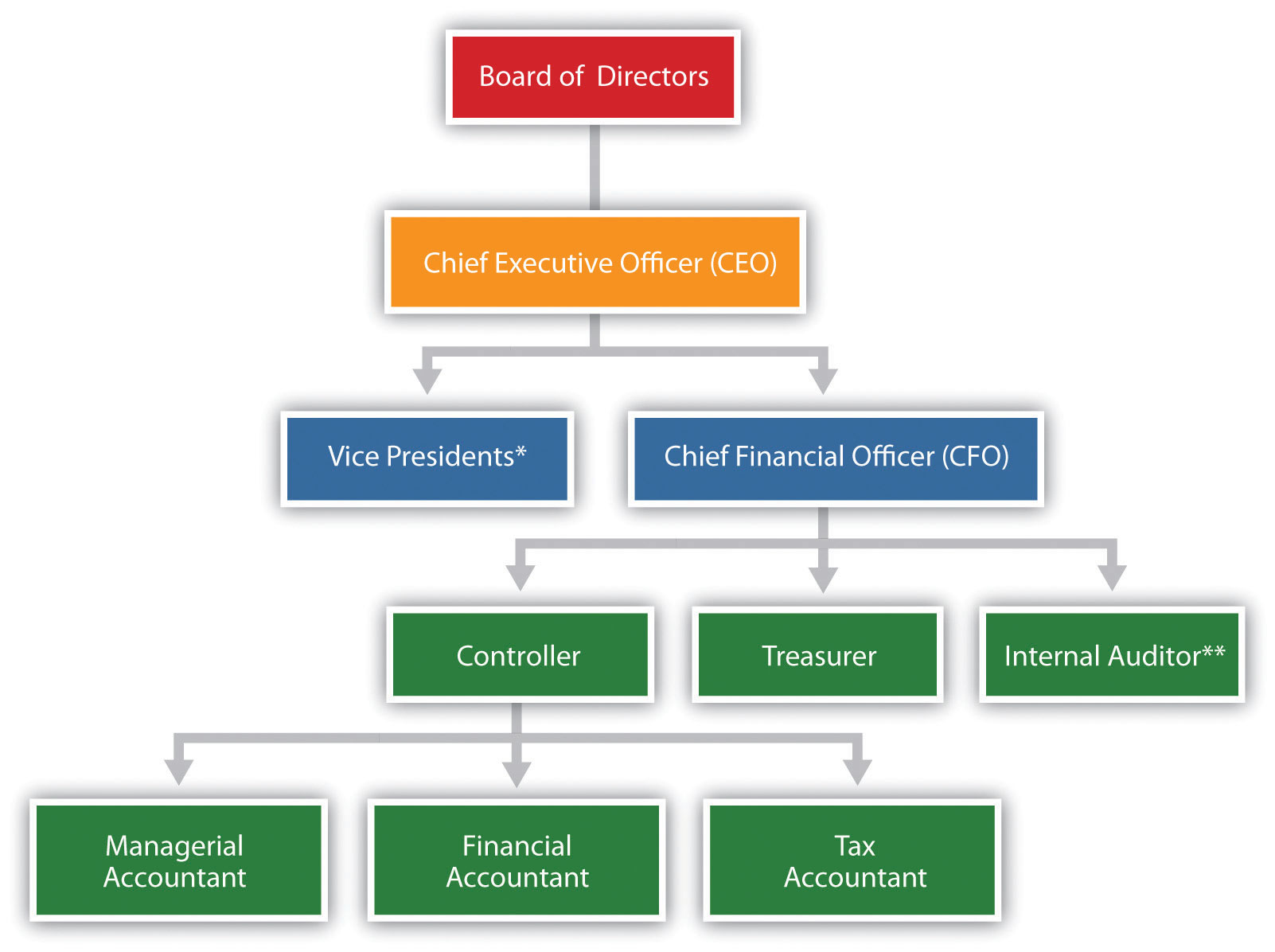
- The head of the finance function of a firm usually has the title of chief financial officer (CFO) and generally reports directly to the firm’s chief executive officer.
- Reporting to the CFO are the treasurer, the controller, and the vice-president of financial management.
- Explain the risk–return trade-off.
- Financial managers try to maximize the wealth of their firm’s shareholders by striking the right balance between risk and return. Often, the decisions that involve the highest potential returns expose the firm to the greatest risks.
- Financial plan
- Define financial plan
- A financial plan is a document that specifies the funds needed by a firm for a given period of time, the timing of cash inflows and outflows, and the most appropriate sources and uses of funds
- What three questions does a financial plan address?
- What funds will be required during the planning period?
- When will funds be needed?
- Where will funds be obtained?
- Explain the steps involved in preparing a financial plan?
- The first step is to forecast sales over a future period of time.
- Second, the financial manager must estimate the expected level of profits over the planning period.
- The final step is to decide on the additional assets needed to support the additional sales.
- Asset management
- Why do firms often choose to invest excess cash in marketable securities?
- Cash in hand earns no rate of return. Excess cash should be invested in marketable securities.
- Marketable securities are low-risk securities that have short maturity dates and can be easily sold in the secondary markets. As a result, they are easily converted into cash when needed.
- What are the two aspects of accounts receivable management?
- The two aspects of accounts receivable management are deciding on an overall credit policy (whether to offer credit and, if so, what terms of credit to offer) and deciding which customers will be offered credit.
- Explain the difference between an expansion decision and a replacement decision?
- An expansion decision involves decisions about offering new products or building or acquiring new production facilities.
- A replacement decision considers whether to replace an existing asset with a new asset.
- Funds and capital structure
- Explain the concept of leverage.
- Leverage is a technique of increasing the rate of return by borrowing funds. But leverage also increases risk.
- Why do firms generally rely more on long-term funds than short-term funds?
- Although short-term funds are generally less expensive than long-term funds, short-term funds expose the firm to additional risks. The cost of short-term funds can vary greatly from year to year. In addition, short-term funds can sometimes be difficult to obtain.
- What is an important factor in deciding on a firm’s dividend policy?
- The main factor in deciding on a firm’s dividend policy is its investment opportunities. Firms with more profitable investment opportunities often pay less in dividends than firms that have fewer such opportunities.
- Short-term financing options
- What are the three sources of short-term funding?
- Trade credit
- Short-term loans from banks and other financial institutions
- Commercial paper
- Explain trade credit.
- Trade credit is extended by suppliers when a buyer agrees to pay for goods and services at a later date. Trade credit is relatively easy to obtain and costs nothing unless a cash discount is offered.
- Why is commercial paper an attractive short-term financing option?
- Commercial paper is an attractive financing option because large amounts of money can be raised at interest rates that are usually lower than the interest rates charged by banks
- Long term financing options
- What is the most common type of security sold privately?
- Corporate debt securities are the most common type of security sold privately.
- Explain venture capital.
- Venture capitalists are important sources of funding, especially for new companies.
- Venture capitalists invest in new companies by taking an ownership position. If the business succeeds, venture capitalists can earn large profits.
- What is a sovereign wealth fund?
- A sovereign wealth fund is a government-owned investment company. These companies invest in a variety of financial and real assets, such as real estate. Although most investments are based on the best risk–return trade-off, investment decisions are also influenced by political, social, and strategic considerations
- Mergers, acquisitions, buyouts, and divestitures.
- Define synergy.
- Synergy is the term used to describe the benefits produced by a merger or acquisition. It refers to the idea that the combined firm is worth more than the buyer firm and the target firm are worth individually.
- What is an LBO?
- An LBO (leveraged buyout) occurs when public shareholders are bought out and the firm reverts to private status. LBOs are usually financed with large amounts of borrowed money.
- What are the two types of divestitures?
- In a selloff, assets are sold by one firm to another firm.
- In a spinoff, a new firm is created from the assets divested. Shareholders of the divesting firm become shareholders of the new firm.
Lecture §
Active Studying §
Summarize today’s lecture §
- [::Most important/focused topic]
- [::Most difficult part, why, how to resolve]
What part I didn’t understand, next step actions? §