Reading §
Chapter 5 §
- Small business
- Describe the characteristics of a small business (by Industry Canada).
- Independently owned,
employees < 100, revenues < $2 million
- In what industries do small business play a significant role?
- Provide jobs in construction, agriculture, wholesale trade, services, retail trade
- Discuss the contributions of small business to the economy
- What are the 3 key ways small business contribute?
- Provide new jobs, create new industries, innovate new ideas
- How are new industries formed
- When small business shift focus to meet consumer interest’s and preferences
- When both business and consumers see a need for change
- Discuss why small business fail ^428ef2
- What are some percentages for small business survival rate
- 96% in business for 1 year (4% close after 1 year)
- 85% in business for 2 year (15% close after 2 year)
- 70% in business for 5 year (30% fail within 5 years)
- What are the 3 main cause of small-business failure
- Management inexperience
- Inadequate financing
- Difficulty meeting government regulations
- Describe the features of an effective business plan
- What are the 5 main sections of a business plan?
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Financial section
- Marketing section
- Resumes for the principals
- Importance for business plan. ^a9f6d6
- Writes out all the reasons a business can be successful (vision of founders & why the company is unique)
- Document needed to obtain financing
- Creates a framework for the organization
- Identify the assistance available for small business
- What are the various ways the BDC (Business Development Bank of Canada) helps small business.
- Provides long-term financial assistance and management counselling
- Provides information, advice, training to owners
- What are business incubators?
- Programs community agencies set up to help small business (low-cost rental space, shared clerical staff, shared office equipment)
- Why are small business good opportunism for women?
- Helps with family and work balance
- Explain franchising
- Differentiate franchisor with franchisee
- Franchisor: permits a small-business owner (franchisee) to market and sell the franchisor’s product under its brand name in return for a fee
- How does franchising benefit both parties
- Franchisor: opportunities for expansion & greater profits
- Franchise: name recognition, quick startup, support for the franchisor, freedom of small-business ownership
- Outline the forms of private business ownership
- What are the 3 legal forms of business ownership
- Sole proprietorship
- Owned and operated by one person
Pros: easy to set up and offer great operating flexibilityCons: personally liable for all firm’s debts and legal responsibilities
- Partnership
- Two or more individuals share responsibility for owning and running
Pros: easy to set upCons: do not protect either partner from liability
- Corporations ^8d7dbe
- Separate legal entity from its owners; investors receive shares from stock in the firm
Pros: owners have no legal and financial liability beyond individual investmentsCons: hard to set up
- What is the main characteristic of a not-for-profit corporation?
- Goal does not include pursuing a profit
- separate legal provisions
- Exempt from paying income taxes
- Describe public and collective business ownership
- Public ownership: a unit or agency owns and operates an organization
- Collective ownership: owners work together to operate all or part of the activities in their firm
- Allows small firms to pool resources, share equipment, experitise, and help each other
- Discuss the organizational structure of corporations
- What are the 2 key elements of the incorporation process (成立过程)?
- Where to incorporate
- The corporate charter (公司章程)
- Identify the 5 main levels of corporate ownership and management
- Shareholders
- Board of directors
- Top management (CEO, CFO…)
- Middle management
- supervisory management
- Describe mergers (并购), acquisitions (收购), and joint ventures (合资企业).
- Merger: >2 firms combine to form one company
Vertical merger: combines firms operating at different levels in production and marketing process
- Horizontal merger: joins firms int he same industry
- Conglomerate merger: combines unrelated firms
- Acquisitions: firms purchase another
- The buyer acquires the firm’s property & assets AND debt
- Joint venture: partnership between companies for a specific activity
Chapter 6 §
- Describe what is an entrepreneur and its different types.
- Explain why people choose to became entrepreneurs ^74557a
- What are the 4 main reasons people choose to become entrepreneurs?
- Be their own boos
- Greater financial success
- More control over job security
- Enhance quality of life
- What factors affect the entrepreneur’s job security?
- Depends on decisions of customers and investors
- Depends on cooperation nd commitment of their employees
- Discuss factors support and expand opportunities for entrepreneurs.
- Factors
- Favourable public perception
- Availability of financing
- Falling cost
- Widespread availability of technology
- Globalization
- Entrepreneurship education
- Changing demographic and economic trends
- Describe difference with entrepreneurs in different countries, new opportunities with globalization
- >9% starting or managing new business
- Globalization allows marketing aboard, hire international talent
- Many Canadian companies have international sales (especially with US)
- Identity educational factors that can help expand opportunities.
- Entrepreneurship majors
- Entrepreneurship emphasis (创业重点)
- Courses to start business
- Teaching in entrepreneurship by organizations
- Identity the traits of successful entrepreneurs ^3e009c
- Define entrepreneurs vision
- Overall idea for how to make their business idea a success
- Importance for high energy level and strong need for achievement
- Energy level: entrepreneurs need to work long hours (small staff number)
- Need for achievement: helps them enjoy challenge for reaching difficult goals
- Summarize the process of starting a new venture (风险投资)
- Process
- Choose idea
--> business plan --> obtain financing --> organize resources
- What are the 2 most important considerations for choosing an idea?
- Something one love/good at
- Meets the need in marketplace
- Differentiate debit financing & equity financing ^b6f84a
- Debt financing: money borrowed that must be repaid
- Equity financing: exchange of ownership shares for money
- Explain intrapreneurship (内部创业)
- Why do large companies support intrapreneurship?
- Keep entrepreneurs spirit alive to promote innovation and change
- What is a skunkworks
- A skunkworks project initiated by an employee who has an idea and then recruits resources from within the compnay to turn the idea into a commercial product
Lecture §
PDF:
- “Business and society”
- Wealth creation
- What is wealth and what is a wealth creation
- Wealth: the annual produce of the land and labour of society (Adam Smith)
- Wealth creation
- What is the Diamond of Sustainable Growth, and its four factors?
- What is required to create wealth
- Interdependence of business
- The diamond
- How is wealth created
- Product/service with
sell > cost
- Trade to get pay for what you have and sell you what you want
-
Case study: house sells §
```ad-case
- Buy a house, renovate it , sell it with a higher price
- Print, stage, add asset, clean up the house
```
- Forms of business ownership
- What are the 4 forms of private business ownership
- Proprietorship
- People and business combined together (personal level)
- LLP (limited liability partnership)
- Sole proprietorship
- Partner proprietorship
Prons: bring different things onto the table, risk is reduced, ★ partnership agreement (written)
- Cooperation
- Not-for-profit cooperation?
Pros and Cons for operation as a corporation
Pros
- Limited liability
- Business are separate from personal losses
- Taxes are separate from personal filings
- Easier to change ownership
- Perpetual life (business don’t die with owner)
- Easier to attract employee
Cons
- Double taxation (corporate tax, personal tax)
- Compliance to meet regulatory rules
- Higher startup cost, more paper work
- Less flexible
- What is the basic structure for corporate management
- Shareholders
- What is the difference between preferred share and common share
- Preferred stock gives no voting rights to shareholders while common stock does
- Can be co-owned
- Preferred shares
- “More secure”, limited to dividend
- ★ What are some characteristics of preferred shareholders (exceptions, not by default)
- Convertible (common share can be change to preferred share with a certain ratio)
- Redeemable (refundable)
- Participating (share the leftovers of dividend)
- Cumulative (dividend are cumulative, no interest)
- Dividend does has to be pay every year
- Dividend: leftover cash/income in company
- Callable (company choose to refund)
- Common shares
- “Real owners” earned the most, lose the most, not limited devident
- Board of directors
- Elected by the common shareholder
- Corporate offices & managers
- Selected by board of directors
- What are some characteristic of franchising
- Franchising agreements exist between franchisee and franchisor
- Canada has 76,000 individual franchise businesses operating under 900 different brand names
- These franchises employ more than one million Canadians
- More than $100 billion in sales each year
- Franchising overseas is a growing
- Franchisees does not compete with each other
- ★
Pros and Cons for franchising
Pros:
- Existing supply chain
- Existing business plan
- Lower risk
- Existing name recognition
- Easier to hire
- Can be easily adjusted for local market
- Prior performance record
- Tested management program
- Savings through volume purchases
Cons:
- Franchisee loss some control due to demand of franchisor (regulation limitation)
- Connected regulation (negative branding)
- High investment
- Pay Future payments (royalties)
- Has to be set up as a franchise
- Starting a business
- Why to make BP
- Help contemporary entrepreneurs prepare enough resources and stay focused on key objectives
- What are 3 financing strategy for starting business
- Seed capital: initial funding needed to launch a new vendor
- ★ Debit & Equity financing
- Debt: borrow money, has to be repaid (legal obligation)
- Credit cards
- Family and friends
- Bank loans
- Finance companies
- Interest (tax deductible)
- Higher risk involved (bankrupt)
- Equity: sell ownership, don’t has to be repaid
- Venture capitalists
- Angel investors
- Dividend (not tax deductible)
- Why small business fail (3+1 major reasons).
- Lack of business plan
- Example for business regulation
- Entrepreneurship
- Characteristics of entrepreneurs
- Having a vision
- High energy level
- Need achieve
- Optimism
- Tolerance for failure
- Creativity
- Tolerance for ambiguity
- Internal locus of control
- 4 reasons people choose to become entrepreneurs
- What are some challenges for entrepreneurs
- Highest risk/ highest return activity in business
- Great difficulties in raising investment funds for a brazen, new idea
- Reality is nearly always very different from what was planned
- High failure rate - even after initial funding secured
- Small business vs. entrepreneurial businesses
- Size
- Small b. remains small; entrepreneurial b. start small, expect to grow big
- Age
- Small b. remains stable, entrepreneurial b. grow up
- Growth goals
- Small b. not expected to grow
- Growth is priority for entrepreneurial b.
- David Birch Model
-
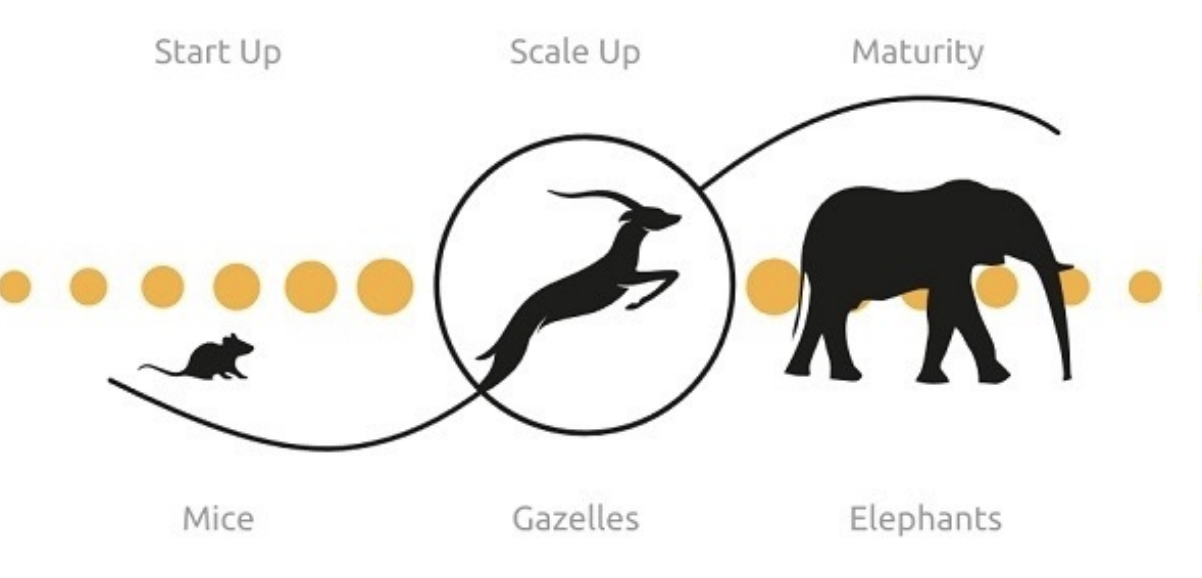
- Mice
Pros: can typically change direction quicklyCons: not powerful- Many do not aspire to grow large, so long as they remain attractively profitable
- Gazelles
Pros: can change directions quicklyCons: more powerful- A firm that seeks rapid growth AND above average profitability (>20% a year for 4 years, doubling in size)
- Often includes a radical business innovation/ implementation of new technology
- Elephants
Pros: very powerful, dominate in marketCons: cannot change directions quickly- “Fortune 500”
- Considerable overall marketplace power
- Difficult for them to change direction quickly
- Collectively, they have fired more people than they have hired in the past 25 year
-
Creating wealth during a pandemic (case study) §
```ad-case
Q: Is it a good to invest in Cheesecake Factory in COVID-19 **today**?
- Given statistic
- Revenue from 2020 droped
- Revenue from 2021 raised back backup
- Profit when to negative in 2020
- Profit recovered back to positive in 2021 (not stable even before covid)
- Stock prices droped in 2020, raised until 2023, droped throughout 2022
- Analysis
- Debate
- Revange travel (already done in 2022, still remaining in 2023)?
- Partner with delivery (?)
- Reasons for a good time:
- Expanded operations in 2021
- Already spent money, ready to collect profit
- Pandanmic killed competition, if demand come back, this would benefit their sells with fewer competition
- Reasons for not a good time:
- Possibility of entering another recession
- Lossed money during 2021, are they able to recover?
- Malls are closed (down), negative effect for the factory
- Competitors have already fired backrupt
- Fined by ... for not misleading investors
- Not able to pay rent for a period of time
- New trend for moving to healier diet
```
Active Studying §
Summarize today’s lecture §
- [::Most important/focused topic] Cooperation, Entrepreneur
- [::Most difficult part, why, how to resolve] Class participation
- Come with question prepared, raise hand quickly, follow with lecture quickly, raise hand with confidence
What part I didn’t understand, next step actions? §
