Lecture §
PDF:- Memory Processes: Encoding, Consolidation and Retrieval
- What (2) strategies are effective and not effective for memory
encoding?
- Effective:
- Relation association to prior knowledge
- Understanding of the concept (depth of processing)
- Low-level processing is harder to encode
- High-level processing is easier to encode
- Not effective: simple repetition
- What does hippocampus play in memory
consolidation?
- Systematic Consolidation
- How can ECT effect reconsolidation?
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) severely disrupts recently-acquired memories in humans (and animals)
- What did Testing Effect suggest about memory
retrival?
- Active recalling (practice test) increase recall accuracy
- Desirable difficulty: difficult but successful retrievals are better for memory than easier successful retrievals
More cues -> Better recall (less difficulty)
- Brain Substrates
- Where are the Semantic Memory stored in the brain?
- Which area of the brain is Consolidation depended on
- Standard consolidation theory
- During learning, the MTL relays information to the cortex
- Over time, the cortex gets the message and the memories become independent of the MTL
- Multiple memory trace theory
- The MTL helps organize together the distributed semantic facts into specific episodic memories
- True episodic memories are never fully independent of the MTL
- What does the Frontal Lobe play in Consolidation?
- What does sleep contribute to Consolidation?
- Cells in the hippocampus “replay” the the activity of memory during the day
- Reactivation is important for consolidating important memories throughout the cortex (and not consolidating unimportant memories)
- How does LTP in the Hippocampus affect memory
- | Diagram | Structure Importance |
|---------|----------------------|
|
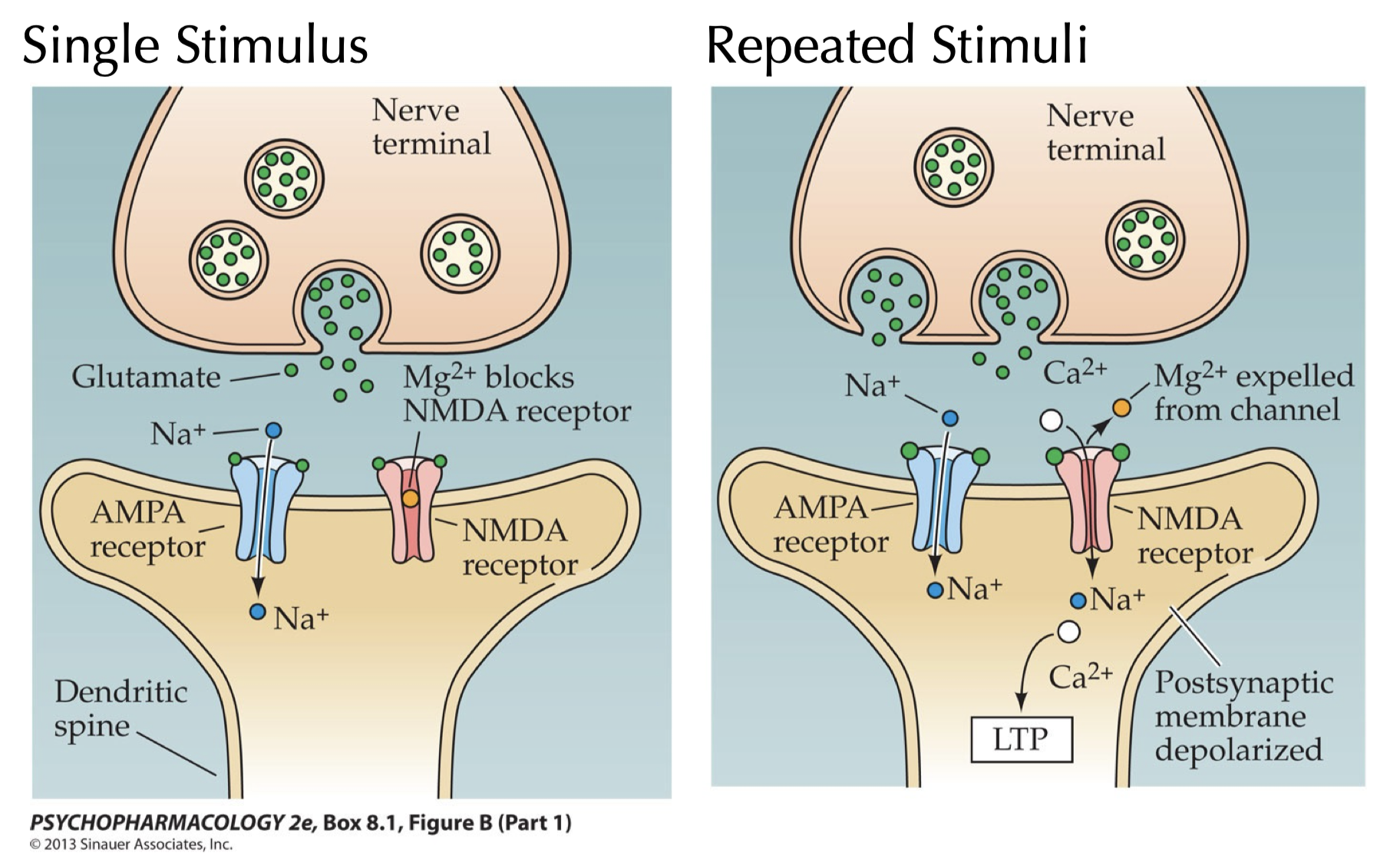 | 1. Glutamate release from terminal
| 1. Glutamate release from terminal
2. Bind to AMPA receptor
3. Na+ enters receptive cell
4. Cause depolarization in receptive cell
5. Enough depolarization cause Mg2+ pops out of NMDA receptor
6. Ca2+ enters receptive cell |
| 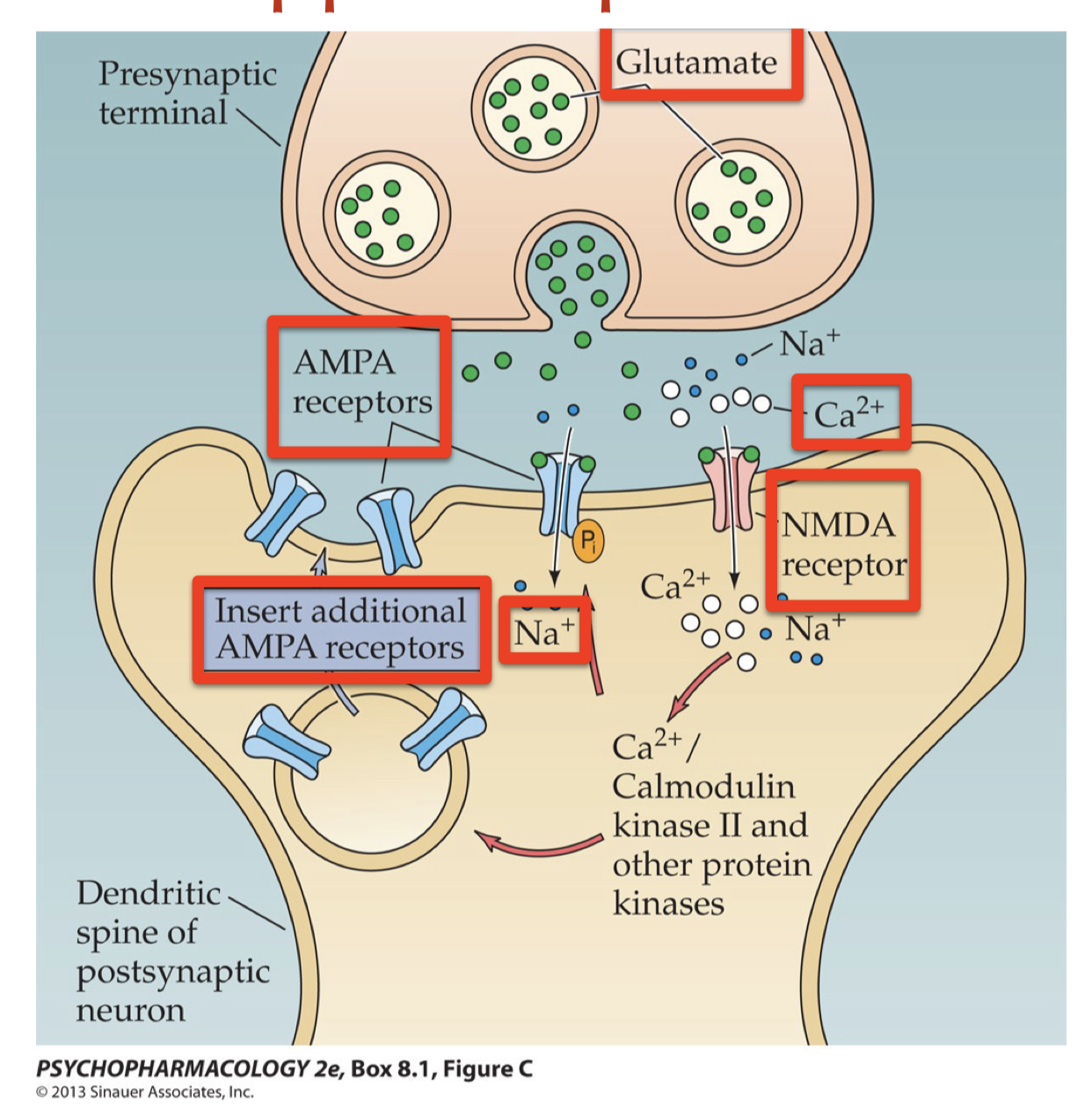 | 1. Calcium causes insertion of additional AMPA receptors
| 1. Calcium causes insertion of additional AMPA receptors
2. Enhance memory
3. Joe Tsien’s Doogie mouse (1999) shows that memory is enhanced by better object recognition |
 | 1. Glutamate release from terminal
| 1. Glutamate release from terminal  | 1. Calcium causes insertion of additional AMPA receptors
| 1. Calcium causes insertion of additional AMPA receptors